[Soft drinks & Health science]
Kirin and Fujitsu Elucidate a Novel Gut–Brain Axis Mechanism of Citicoline for the First Time Worldwide through AI–Based Analysis and Experimental Validation Leveraging Drug Discovery DX Technology
- CSV
- Research and Technology
December 17, 2025
Kirin Holdings Company, Limited
TOKYO and KANAGAWA, December 17, 2025 - Kirin Holdings Company, Limited (Kirin Holdings) and Fujitsu Limited (Fujitsu) have jointly conducted research on food functionality simulation with the goal of creating new functionalities in food. This research utilized QSP models*1, one of the AI-driven digital transformation (DX) technologies for drug discovery*2, combined with real-world experimental validation. As a result, the study has, for the first time worldwide, identified a previously unknown mechanism within the gut-brain axis*3 associated with citicoline*4, a compound known for its role in supporting cognitive health. This finding was obtained by combining virtual subject simulations based on advanced QSP technologies developed by Fujitsu in collaboration with its partner Nova In Silico SAS (France) with cell-based experimental validation.
Conventional drug discovery has been time-consuming and costly, with limitations in improving confidence in demonstrating efficacy in humans. In recent years, the diversification of medical needs and stricter constraints on animal testing have further increased the demand for efficient R&D. To address these challenges, the introduction of DX technologies utilizing AI and data science has been accelerating. In particular, virtual subject generation and in silico simulation*5 enabled by DX technologies are expected to improve reliability in demonstrating efficacy in humans without animal testing, making their application in food functionality research highly promising.
This study represents a globally pioneering example of the full-scale application of DX technologies in food functionality research. It evaluated novel physiological functions of citicoline by combining AI-based prediction with experimental validation. These findings are expected to accelerate the adoption of AI-driven DX technologies in health science and contribute significantly to realizing a society that promotes longevity and well-being through innovative food solutions.
*1 An abbreviation for Quantitative Systems Pharmacology. An information science approach that integrates physiological and pathophysiological networks into computational models to predict drug activity, therapeutic effects, and systemic effects of nutrients.
*2 A method that uses digital technologies such as AI to comprehensively elucidate interactions between disease-related biological systems and drug discovery candidates, including pharmacokinetics and side effects, through mathematical modeling and computer-based analysis. This approach enables the analysis of large-scale molecular data and efficient identification of new drug candidates.
*3 A bidirectional communication network in which the gut and brain influence each other, interconnected through neural, endocrine, immune, and metabolic pathways.
*4 A compound manufactured by Kyowa Hakko Bio, part of the Kirin Group, and marketed globally since the early 1990s, primarily in Europe and the United States. It is widely used as an ingredient in supplements and beverages designed to support cognitive function, as well as in pharmaceutical formulations. Currently, citicoline is approved only for pharmaceutical use in Japan.
*5 An information science methodology that uses data analysis of biological phenomena to predict biological and pharmacological processes and functionalities through computer-based simulations.
Research Results (Summary)
We collected information on citicoline’s metabolic profile and its action-related receptors from Kirin’s proprietary data and literature reviews. Using DX technology, we constructed a QSP model to evaluate the functional properties of citicoline. Simulations using this model predicted that oral administration of citicoline enhances cholinergic signaling in the gut–nerve axis (Figure 1) and induces a dose-dependent increase in acetylcholine levels within intestinal synapses (Figure 2). In parallel, in vitro experimental validation confirmed that citicoline activates neuronal signaling through the intestinal pathway in a co-culture system of intestinal epithelial cells and neurons (Figure 3).
-
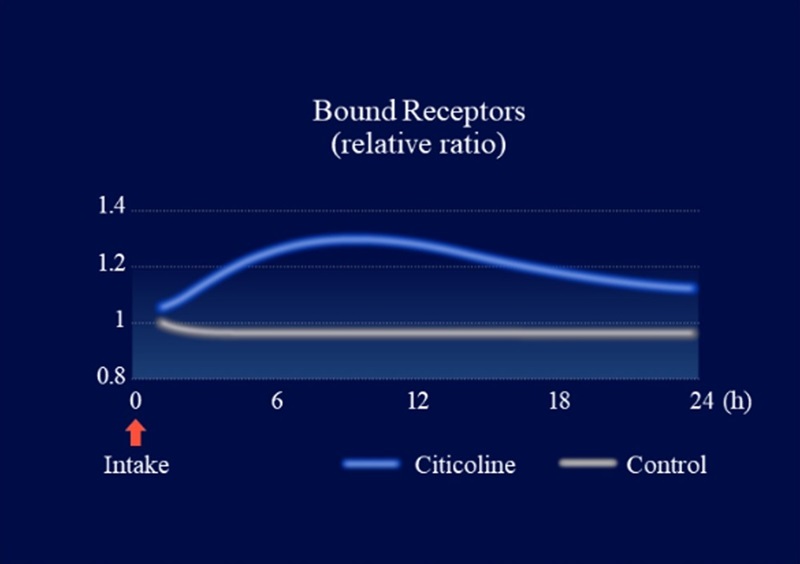
Figure 1. Simulation-based evaluation of ligand-binding cholinergic receptors in enteric neurons using a QSP model
-
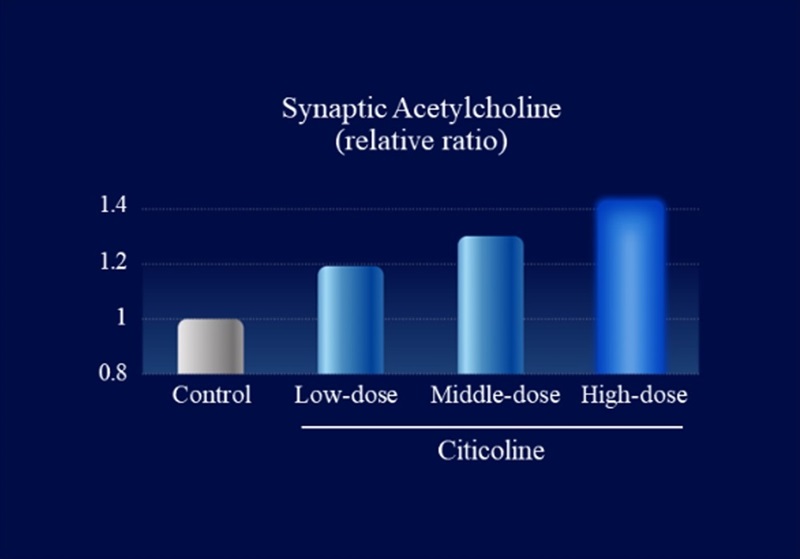
Figure 2. Simulation-based evaluation of acetylcholine levels within intestinal synapses using a QSP model
-
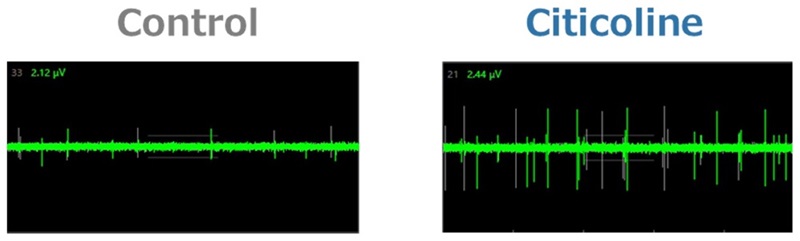
Figure 3. Assessment of Neural Activation with a Microelectrode Array in an Intestinal Epithelial Cell–Neuron Co-culture System
Key Findings
This study predicted, through AI-based analysis, that citicoline could activate neuronal signaling via the gut and validated this prediction in vitro. Furthermore, gut nerves are known to be closely interconnected with the brain. This research has elucidated part of the gut-brain mechanism of citicoline.
Future Outlook
This study represents a globally pioneering example of the full-scale application of DX technology in food functionality research. It provides insights that help elucidate new physiological functions of citicoline, which are essential for supporting brain function, thereby enhancing citicoline’s value as a functional ingredient for health.*6
*6 The information on the food functionality of citicoline is intended for B2B use in overseas markets and is not aimed at domestic consumer promotion.
About Kirin Holdings
Kirin Holdings Company, Limited is an international company that operates in the Food & Beverages domain (Food & Beverages businesses), Pharmaceuticals domain (Pharmaceuticals businesses), and Health Science domain (Health Science business), both in Japan and across the globe.
Kirin Holdings can trace its roots to Japan Brewery, which was established in 1885. Japan Brewery became Kirin Brewery in 1907. Since then, the company has expanded its business with fermentation and biotechnology as its core technologies, and entered the pharmaceutical business in the 1980s, all of which continue to be global growth centers. In 2007, Kirin Holdings was established as a pure holding company and is currently focusing on boosting its Health Science domain.
Under the Kirin Group Vision 2027 (KV 2027), a long-term management plan launched in 2019, the Kirin Group aims to become “A global leader in CSV*, creating value across our world of Food & Beverages to Pharmaceuticals”. Going forward, the Kirin Group will continue to leverage its strengths to create both social and economic value through its businesses, with the aim of achieving sustainable growth in corporate value.
* Creating Shared Value. Combined added value for consumers and society at large.
About Fujitsu
Fujitsu’s purpose is to make the world more sustainable by building trust in society through innovation. As the digital transformation partner of choice for customers around the globe, our 113,000 employees work to resolve some of the greatest challenges facing humanity. Our range of services and solutions draw on five key technologies: AI, Computing, Networks, Data & Security, and Converging Technologies, which we bring together to deliver sustainability transformation. Fujitsu Limited (TSE:6702) reported consolidated revenues of 3.6 trillion yen (US$23 billion) for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2025 and remains the top digital services company in Japan by market share. Find out more: global.fujitsu (https://global.fujitsu/en-global)
AI-Based Research into the Gut-Brain Mechanism of Citicoline
What is Citicoline?
Citicoline is an endogenous compound in the human body that serves as a precursor to phosphatidylcholine, a major constituent of neuronal membranes. It contributes to neuroprotection by supporting the repair and maintenance of brain cell membranes, thereby promoting brain function. As a pharmaceutical agent, citicoline is used to assist recovery after cerebral infarction and to support neurological recovery in conditions such as vascular dementia. As a dietary supplement, it is widely used globally to support memory and attention and promote brain health. Currently, citicoline is approved only for pharmaceutical use in Japan.
Research Findings: Gut-Mediated Mechanism of Citicoline on the Nervous System
Background and Objectives
Conventional drug discovery is time-consuming and costly, with limitations in improving confidence in demonstrating efficacy in humans. In recent years, the diversification of medical needs and stricter constraints on animal testing have further increased the demand for efficient research and development. To address these challenges, the introduction of DX technologies utilizing AI and data science has been accelerating. Specifically, technologies such as virtual subject generation and in silico simulation enabled by DX are expected to improve reliability in demonstrating efficacy in humans without animal testing, making them highly promising for application in food functionality research. This study aimed to evaluate novel functionalities of citicoline by combining AI-based prediction with experimental validation, utilizing QSP technology from Fujitsu and its partner Nova In Silico.
Research Method
Information on citicoline’s metabolic profile and action-related receptors was collected from proprietary data and literature reviews. A QSP model for assessing citicoline’s functionality was constructed by integrating physiological and pathophysiological networks into a computational framework. This model was used to simulate and assess the functionality of orally administered citicoline.
Results
Simulations revealed that oral citicoline intake increases cholinergic signaling activity in the gut–nerve axis (Figure 1). Furthermore, when receptor response to this signal was maximized, acetylcholine levels within synapses of afferent gut nerves increased in a dose-dependent manner (Figure 2). Based on these findings, assessment of neuronal activity using a gut–nerve co-culture model with a microelectrode array confirmed that citicoline activates neuronal signaling via the gut (Figures 3 and 4).
-
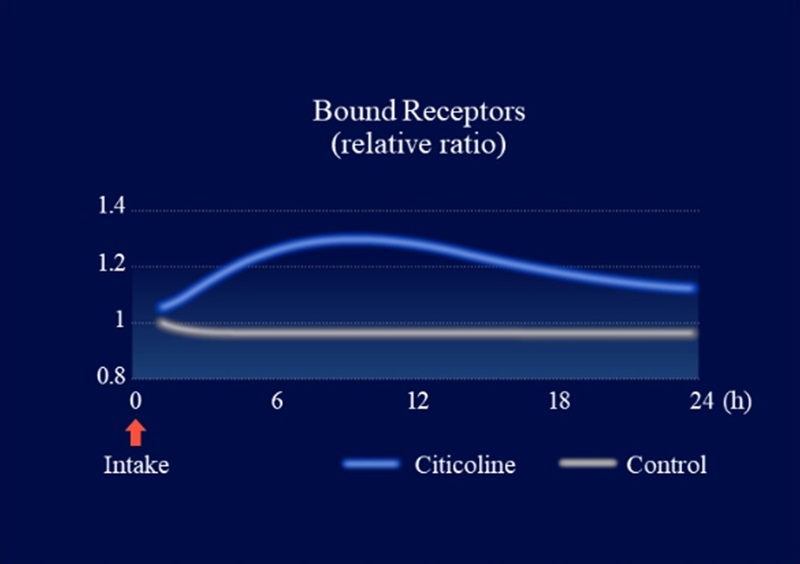
Figure 1. Simulation-based evaluation of ligand-binding cholinergic receptors in enteric neurons using a QSP model
-
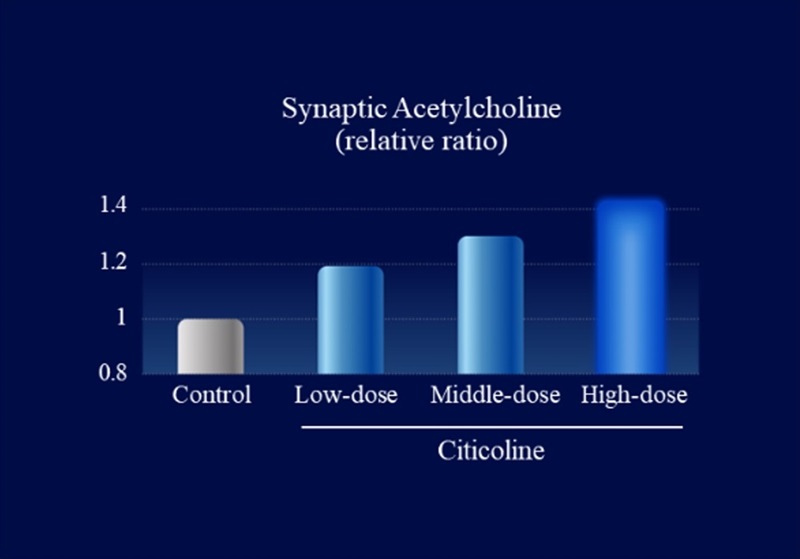
Figure 2. Simulation-based evaluation of acetylcholine levels within intestinal synapses using a QSP model
-

Figure 3. Assessment of Neural Activation with a Microelectrode Array in an Intestinal Epithelial Cell–Neuron Co-culture System
-
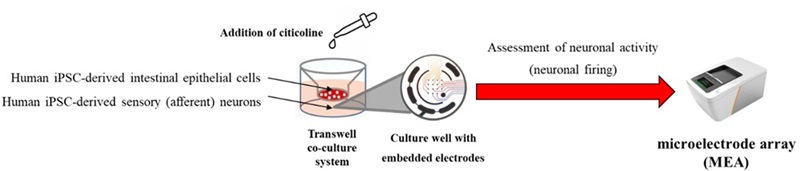
Figure 4. Schematic diagram of the experimental method using a co-culture system of intestinal epithelial cells and neurons
Joint Research Findings
AI-based analysis predicted that citicoline activates afferent neural pathways via the gut, and this prediction was validated through in vitro cell-based experiments. Gut neurons are known to communicate bidirectionally with the brain through pathways such as the vagus nerve, forming the gut-brain axis. This study elucidated part of the gut-brain mechanism of citicoline. Furthermore, this research represents a globally pioneering example of the full-scale application of DX technology in food functionality research. These findings are expected to promote AI-driven DX implementation in health science research and contribute significantly to realizing a healthy, long-lived society through citicoline.
GALLERY
-
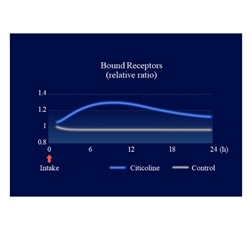
Simulation-based evaluation of ligand-binding cholinergic receptors in enteric neurons using a QSP model
-
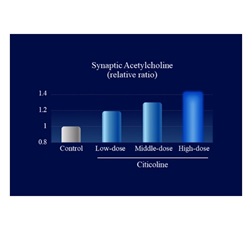
Simulation-based evaluation of acetylcholine levels within intestinal synapses using a QSP model
-
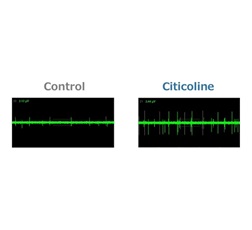
Assessment of Neural Activation with a Microelectrode Array in an Intestinal Epithelial Cell–Neuron Co-culture System
-
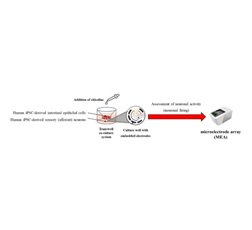
Schematic diagram of the experimental method using a co-culture system of intestinal epithelial cells and neurons