Water Resources
Sustainable use of water resources
Life on earth relies on water and water is an essential resources for the Kirin Group as well. Aslo an indispensable utility for our operation such as cleaning production equipment. It is widely acknowledged that climate change is having a primary impact through water, with consequences including flooding, droughts and changes in rainfall patterns being observed worldwide. There is also an increase in water shortages and pollution. The Kirin Group runs its businesses in various regions in the world; Australia has experienced severe water shortages many times in the past. We know through the business experiences that water risks vary significantly between countries, regions and between present and future scenarios. Since 2014, we have periodically surveyed quantitative water risks of operation sites by using scientific tools and applied findings from the surveys to our business strategies. Not only water risks at at each operation sites, we run scenario analysis based on the TCFD recommendations to understand water risks in areas producing our agricultural raw materials and try countermeasures to the risks. We will go beyond just reducing water usage and try to identify and mitigate our impact on the natural capital of basins as a whole, collaborating with local stakeholders.
Main Activities
- Conservation of water sources at 27 locations in tea farms in Sri Lanka by the end of 2024. Also, we distributed pamphlets to raise awareness for local residents in water source areas (approximately 15,000 people) , telling the importance of water, water conservation, and protection of basin regions.
- In the Corporate Engagement Program held by the Science Based Targets Network to develop scientific approaches and rules for setting targets related to water resources (since 2021).
- A scenario analysis workshop requested by TNFD at New Belgium Brewing in Fort Collins, Colorado (US), where water stress is extremely high (2023: the details of this workshop were published in beta v0.4 of the TNFD Framework).
- Conserving biodiversity and recharging groundwater through “Water Source Conservation Forest Activities.”
Target
Water consumption rate at production sites and breweries with high levels of water stress (Lion)
2025: Less than 2.4kl/kl (CSV commitment)*1
2025: 2.4kl/kl or less (non-financial target)*2
2024: 3.0kl/kl or less (non-financial target)*2
- *1Tooheys Brewery,Castlemaine Perkins Brewery, James Boag Brewery, Pride
- *2Tooheys Brewery,Castlemaine Perkins Brewery, James Boag Brewery
Progress
Lion Water Consumption Rate
Target: 2.4kl/kl or less
Actual results: 3.1kl/kl
Kirin group water risks
The Kirin Group recognises that water risks have the potential to have a significant impact on not only the water resouses at manufacturing sites (operations sites) but also the agricultural products used in production. Therefore, we analyse water risks from two perspectives: the manufacturing site (operations site) and the agricultural procurement perspective. We then utilise this analysis to inform activities that address actual water risks.
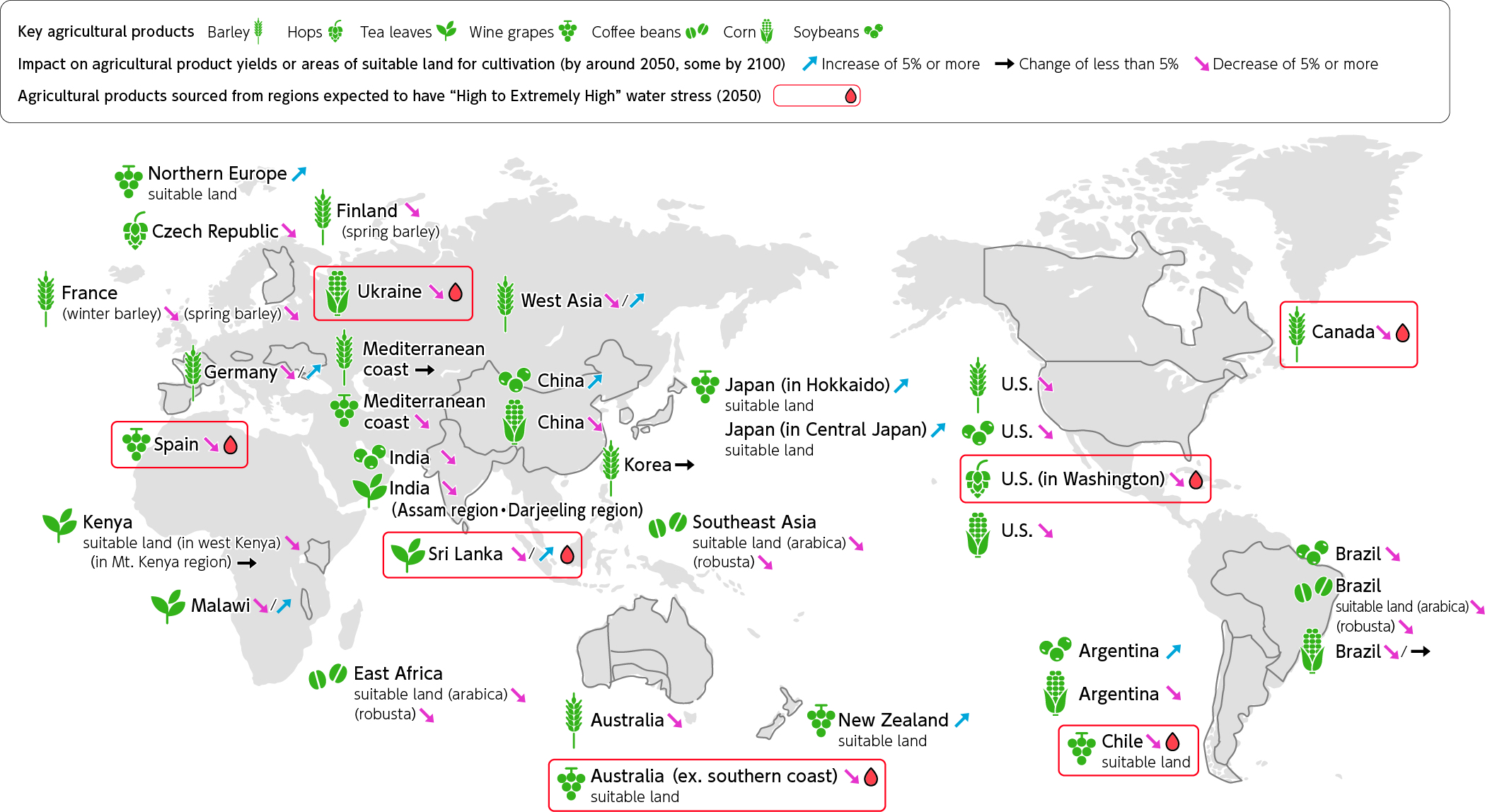
Future Water Risks in Agricultural Procurement
At present, the Kirin Group is focusing on initiatives such as the diversification of suppliers, support for the acquisition of sustainable farm certification, and the development of mass plant propagation technology, and we believe that we are resilient to physical risks to some extent. Even if the Kirin Group achieves our “SBT 1.5°C” target and the “SBT Net-Zero” target, it is becoming increasingly likely that it will be difficult to completely avoid the effects of global warming. Therefore, we intend to consider appropriate adaptation measures and include them in transition plans.
Impact of climate change on yields of key agricultural products and water atress in agricultural production areas around 2050
Water Risks at Manufacturing Sites
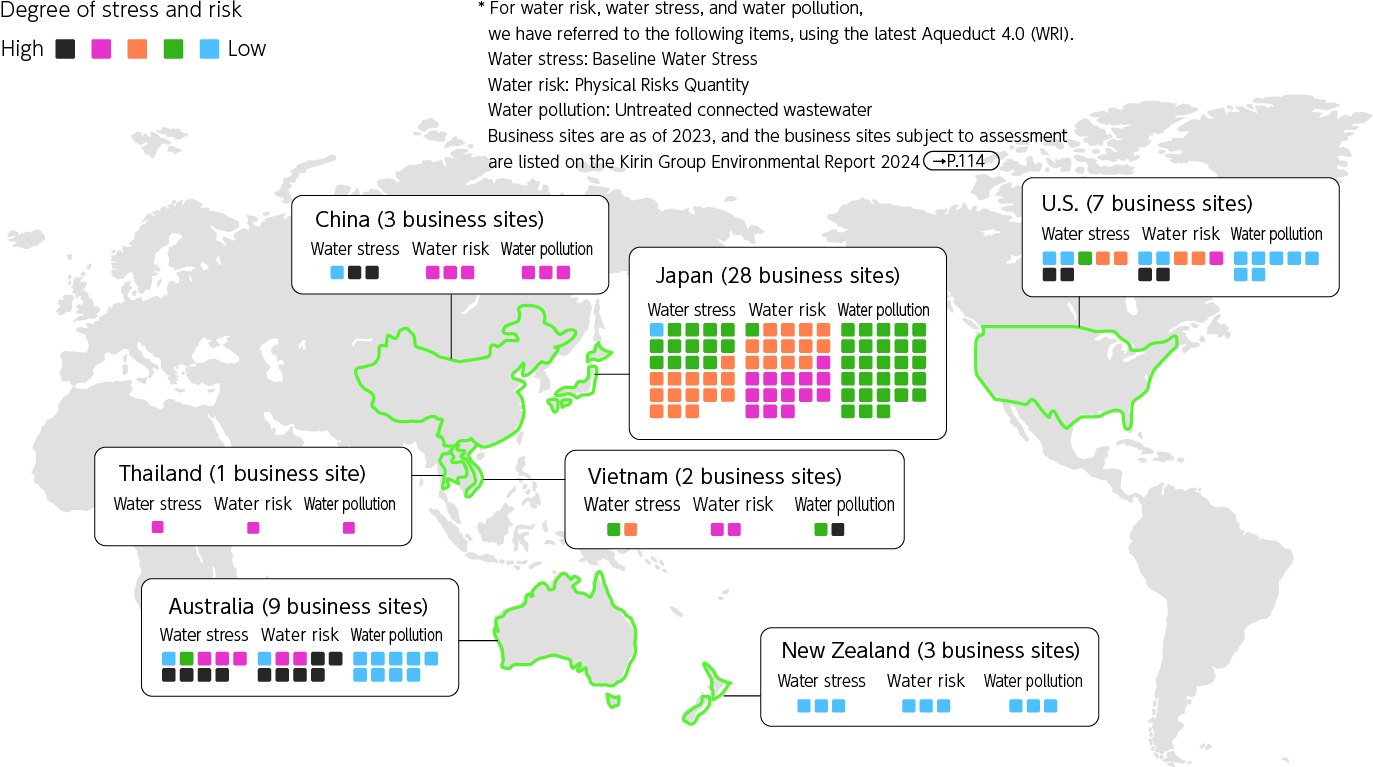
Since 2014, we have been regularly and quantitatively assessing water risks using scientific tools. We set water targets in accordance with the water stress levels at each manufacturing site, with a view to promoting efficient water use. Water risk analyses conducted to date at manufacturing sites indicate particularly high water risks at sites such as Australia. When setting water targets, we determine which manufacturing sites to target based on a thorough understanding of water risks and business realities, gained through investigations and on-site interviews.
Water Stress and Water Risk at Manufacturing Sites
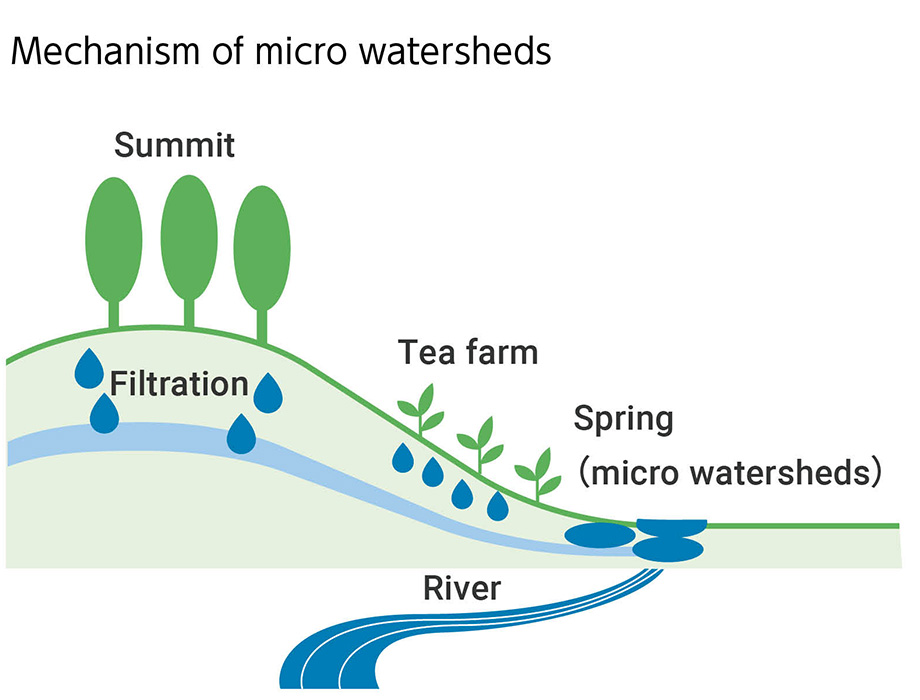
Conservation of Water Sources in Tea Farms
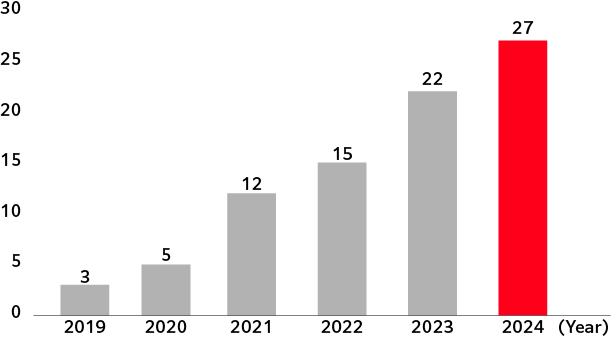
The Kirin Group initiated activities in Sri Lankan black tea production areas identified as having high water stress by “products and water stress in agricultural production areas around 2050,” as the first step toward addressing water challenges in upstream raw material production areas within our value chain. We began conservation activities for water sources within Sri Lankan black tea production areas in 2018, completing the conservation of 27 sites by the end of 2024. We educated 1,750 people living near water sources, telling the necessity of conserving water sources. In addition, we have distributed pamphlets to 15,000 residents, aiming to raise awareness of water conservation and watershed protection.
At the tea plantations of the Sri Lankan highlands, tea trees grow on steep slopes. In such places, rainwater penetrates into the ground and gushes out as springs if strata and other geographic conditions are met. These springs are known as micro watersheds, and can be found in the highlands of central Sri Lanka. In almost all cases, these springs are headwaters of rivers that flow through coastal towns. The watersheds are very valuable sources of water for the cities while occupying a tiny area of central Sri Lanka.
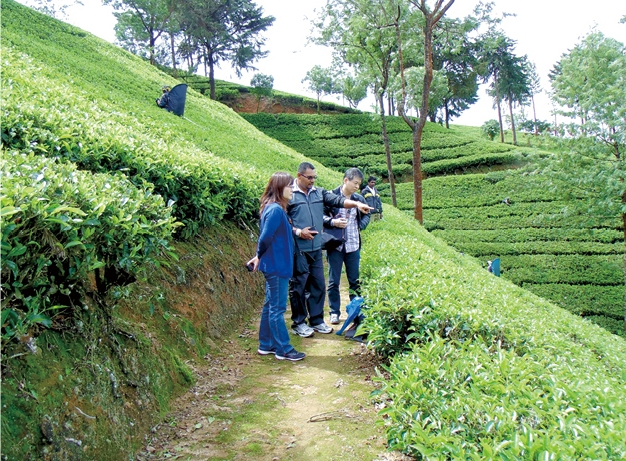
As a part of our supports for Sri Lankan tea farms to acquire Rainforest Alliance certification, we collaborate with farm managers each year. Through discussions with the managers that conservation activities of watersheds were being held up due to lack of funding although the Sri Lankan government recognized importance of micro watersheds and was willing to conserve them. Therefore, in 2018, Kirin Holdings and the Rainforest Alliance started working on activities to conserve watersheds at the farms, now collaborating with Plantation Human Development Trust (PHDT) and Estate Worker Housing Cooperative Societies (EWHCS), affiliated organizations of the Sri Lankan government.
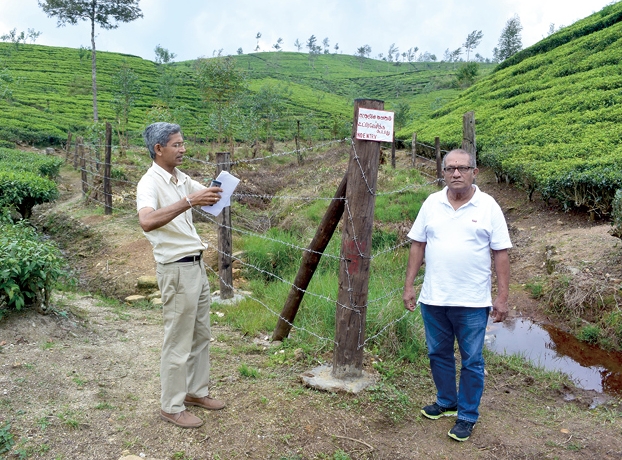
During our most recent visit (March 2024) to farms, we saw progress in conservation efforts, with micro watersheds on farms being fenced off to prevent animal access and inappropriate use of water by others. We are commenced planting native plant species as a natural buffer around the watershed. We expect that the species will provide a diversity of vegetation at tea farms, which currently have a single crop, and prevent soil of mountain slope from flowing down to water sources as a result of torrential rain.
Number of areas where water sources were conserved among Sri Lankan tea farms



Education programs to teach the value of water
The Kirin Group is conducting an education program to teach residents living near water sources about the importance of water and the functions of micro watersheds. At some farms, we are also working to incorporate our educational programs as a part of curriculums of nurseries for children of tea pluckers and elementary schools. We have provided the program to 15,000 people, our initial target, and plan to expand the program further.


Production
Introduction of reverse osmosis (RO) water recycling plant at Water-Scarce Regions
As shown in “Water stress and risk at production sites,” Australia faces chronic water scarcity challenges unlike water-rich Japan.
For example, in Sydney, New South Wales, there is a high risk of drought, and a significant amount of water is used for industrial purposes rather than daily living, necessitating water conservation in the business sector. The Kirin Group aims to reduce water use in water-scarce regions and has set water use intensity targets at Tooheys Brewery, Castlemaine Perkins Brewery, James Boag Brewery, and Pride. To further accelerate these efforts, we have set a target to construct and expand facilities in Australia that purify and reuse water used in breweries (Reverse Osmosis (RO) Water Recycling Plants). Introducing RO water recycling plants in water-scarce regions significantly contributes to water-dependent communities and natural environments. The Kirin Group has installed reverse osmosis (RO) water recycling plants at its Castlemaine Perkins Brewery and Tooheys Brewery, both located in water-scarce regions, by 2024. The recycled water is used for equipment cleaning and other purposes. This facility’s introduction allows for the reuse of approximately 270 million liters of water annually, contributing to wate conservation. This amount is equivalent to filling 108 Olympic swimming pools. Additionally, a $7.2 million investment will save over $700,000 in annual water bills.

Management in the production process
In our production process, we use a lot of water in cleaning and sterilizing processes. We have established management system to strictly control quality of the cleaning processes and water consumption by optimizing flow rate and other parameters. We also actively promote reuse of water, considering characteristics of processes.
For example, the rinsing water that we use in the final cleaning step of a equipment is relatively clean, so we can use it again for the initial cleaning step of other equipment. In this way, the water used for cleaning is cascaded for repeated use according to water quality. In order to ensure that equipments are appropriately cleaned, it is necessary to know how to use the equipment, such as how to balance the amount of water that can be recovered with the amount of water that is used, and how to time the process. The Kirin Group is achieving a high level of water conservation by accumulating best practices and sharing them among production sites.
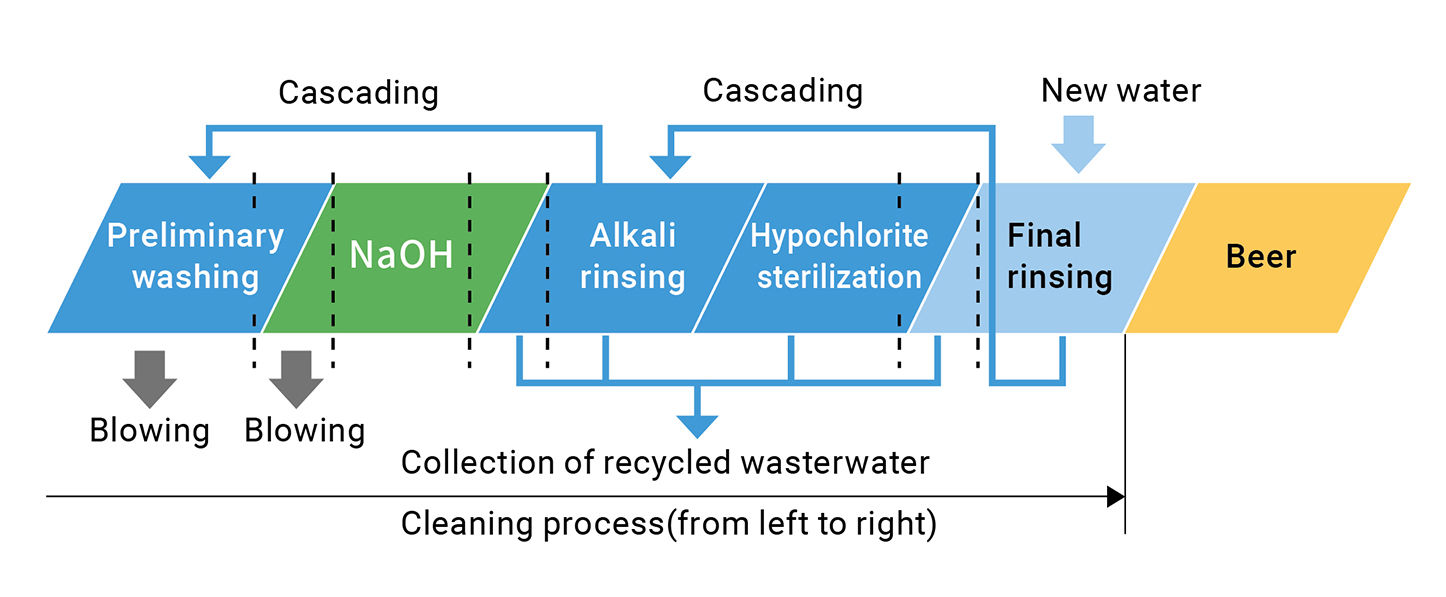
In 2009, Lion partnered with the government of Queensland, Australia, where water stress is extremely high, to install a reverse osmosis (RO) filter at the Castlemaine Perkins Brewery, to minimize water use in brewery. Lion introduced this filter in order to reduce 50% of fresh water usage in the brewery by recycling wastewater. The brewery uses treated water by RO in non-product related processes, such as cleaning, cooling, and pasteurizing. Lion is leading sustainable water use in Kirin Group.
Water Source Forest Conservation Activities
“Water Source Forest Conservation Activities”, an activity to protect water source forests at our plants, began in 1999 with the industry's first forest in the Tanzawa area of Kanagawa Prefecture, which is the source of water for the Kirin Brewery Yokohama Plant, and continues today at 11 locations throughout Japan. Based on medium- and long-term agreements with local governments and related organizations that manage water source forests, we have planted trees, cleared undergrowth and branches, and thinned trees, and many of our forests are now bright and lush. In some locations, customers are invited to participate in these activities.
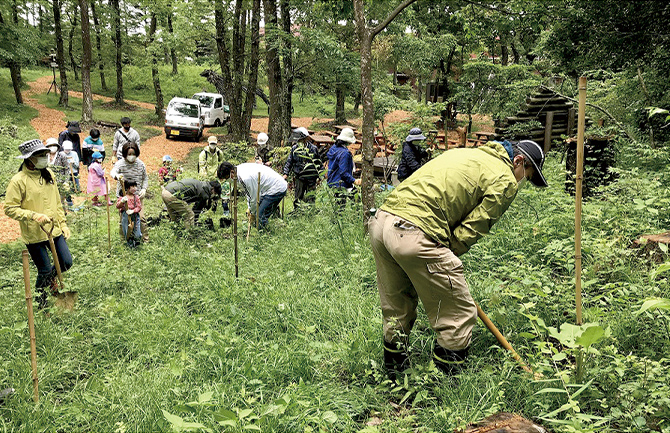

Grassland conservation activities to recharge groundwater
Yatsushiro Plant, one of production sites of Mercian, sent its three employees to “Aso Grassland Restoration Project” which aims to make Aso district a World Heritage Site. The project supports controlled open burning of grassland, a traditional methodology to maintain quality of grasslands. The methodology enables Aso district, where Yatsushiro Plant sources its water, to secure abundant groundwater. Maintaining grasslands not only nurtures groundwater, but also protects habitats for a wide variety of flora and fauna, including endangered species.
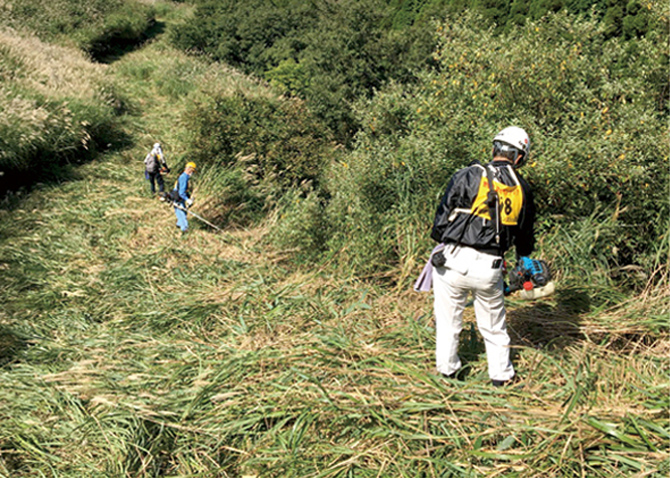
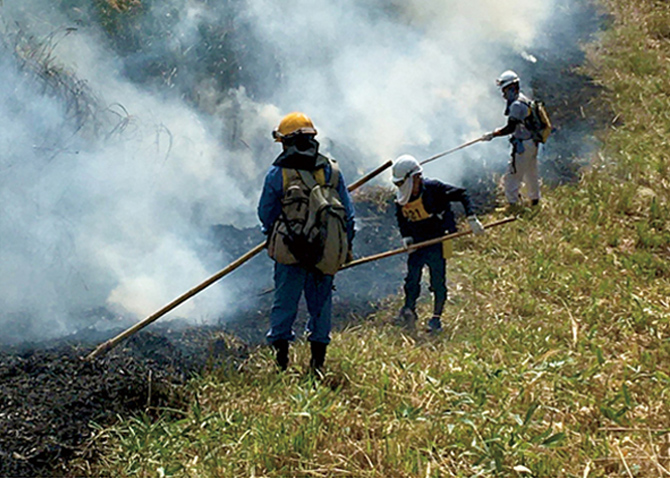


Environmental protection activities in basin regions
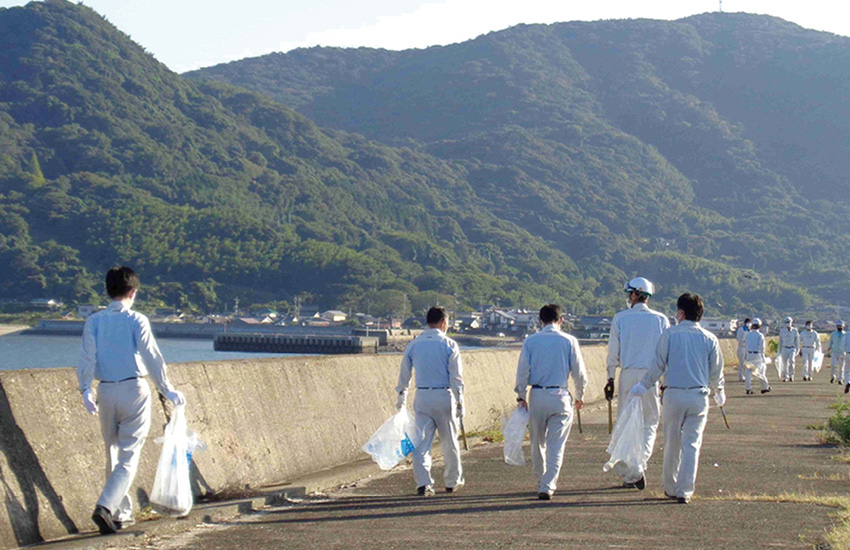
At the various production plants of the Kirin Group, we are conducting a range of environmental protection activities, particularly riverside clean-up activities in cooperation with local governments and NGOs. At our breweries and plants, including those of Kirin Brewery, Kirin Beverage, Mercian, Kyowa Kirin, and Koiwai Dairy Products, we engage with local environmental activities, focusing on rivers where we intake water for production and other nearby rivers.
At Yamaguchi Production Center of Kyowa Hakko Bio, employees conduct clean-up activities in the waters off Hyakken, a port facility where chemicals and glucose solutions are unloaded.

Key Data Related to Water Resources
Metrics and targets
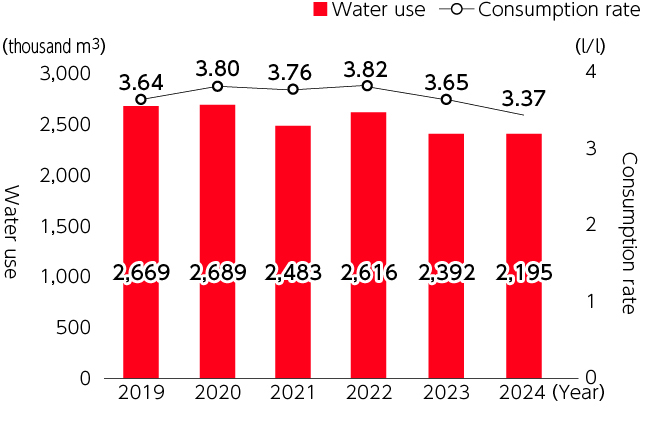
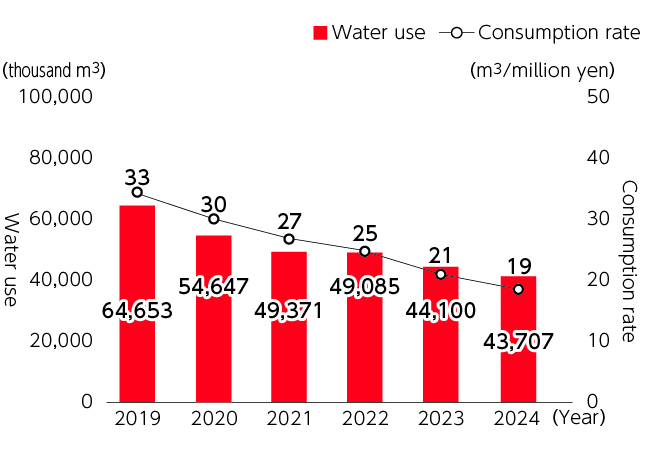
Water use and consumption rate
(water use / production volume)of Lion(Oceania region)
Water use and consumption rate
(water use / sales revenue)of entire Group
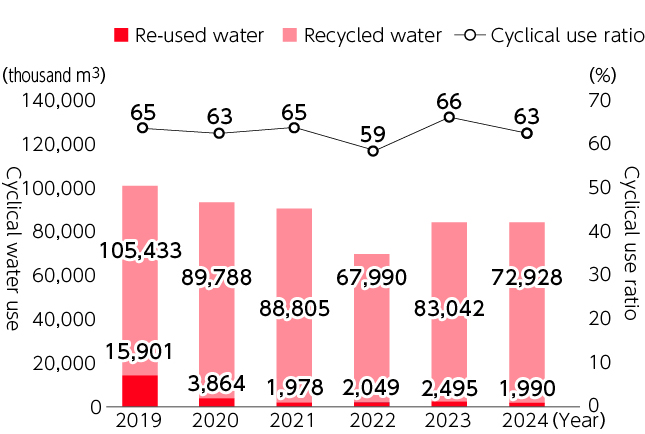
Cyclical water use and cyclical use ratio
(cyclical use / (tap water use + cyclical use))of entire Group