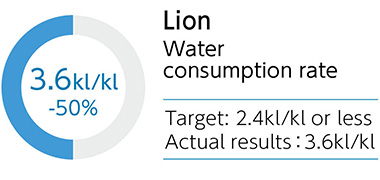Sustainable use of water resources
Sustainable use of water resources
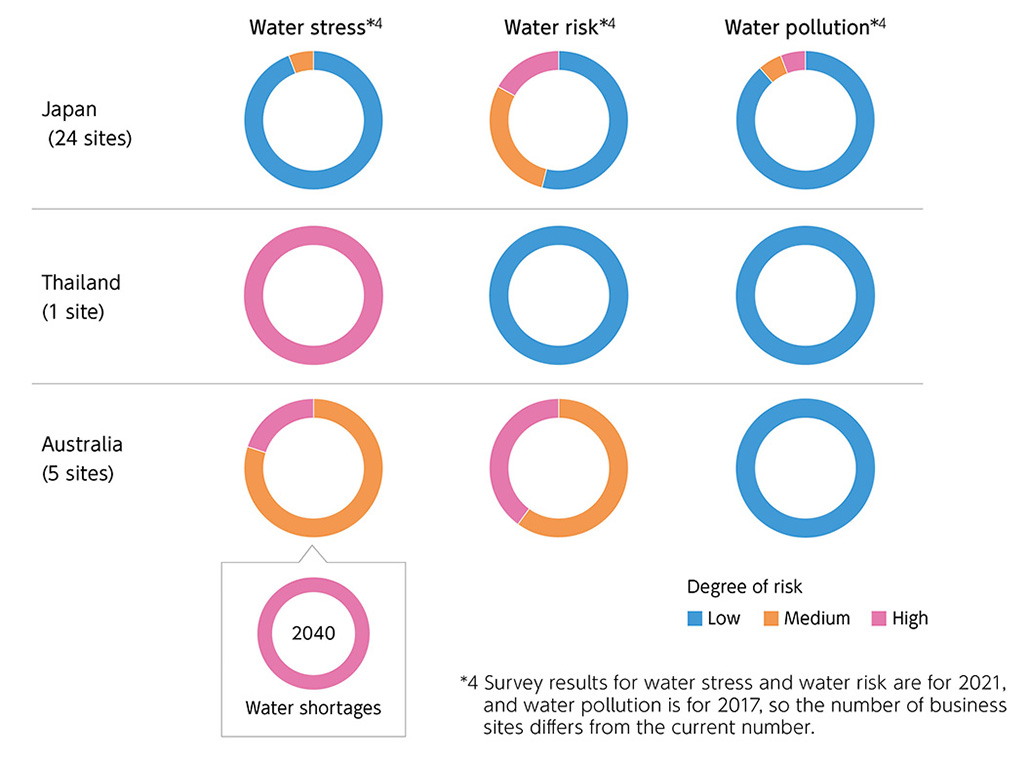
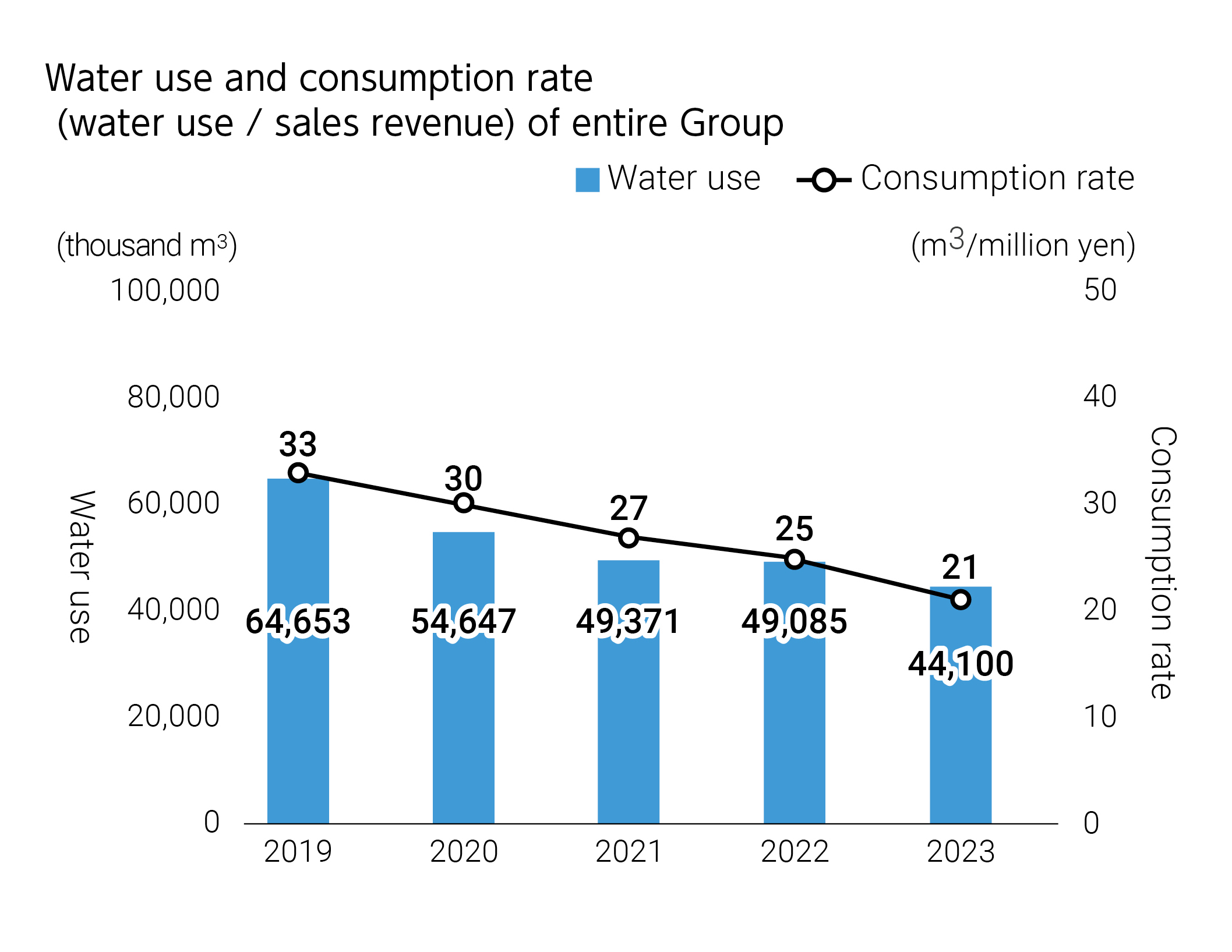
Water is not only an essential raw material for the Kirin Group, but is also an indispensable resource for cleaning our production facilities, etc. The Kirin Group has large businesses in both Japan, where water stress is low, and Australia, which has experienced severe water shortages many times in the past. We have understood from early on that water risks and water stress vary greatly between countries and regions. Since 2014, we have used scientific tools to regularly and quantitatively ascertain water risk and stress, and have used water efficiently in accordance with the level of water stress at each business site. We are conducting a scenario analysis based on the TCFD recommendations to study and identify water risks in areas producing agricultural raw materials, and testing countermeasures in areas where we can implement such measures. Looking ahead, we plan not simply to conserve water, but also to identify our impact on the natural capital of basins as a whole and work with our stakeholders to set targets to enable us to reduce our impact.
Main Activities
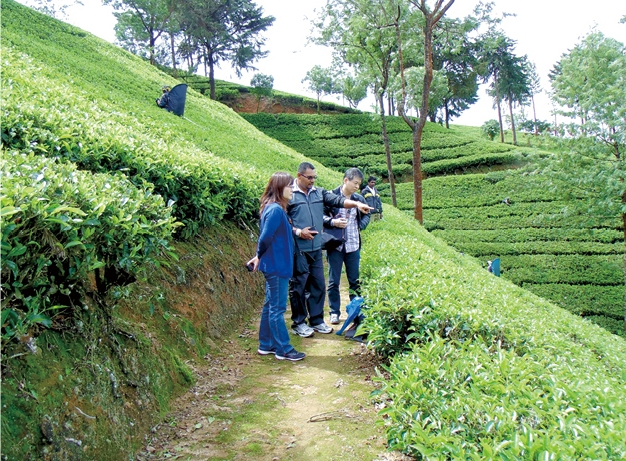
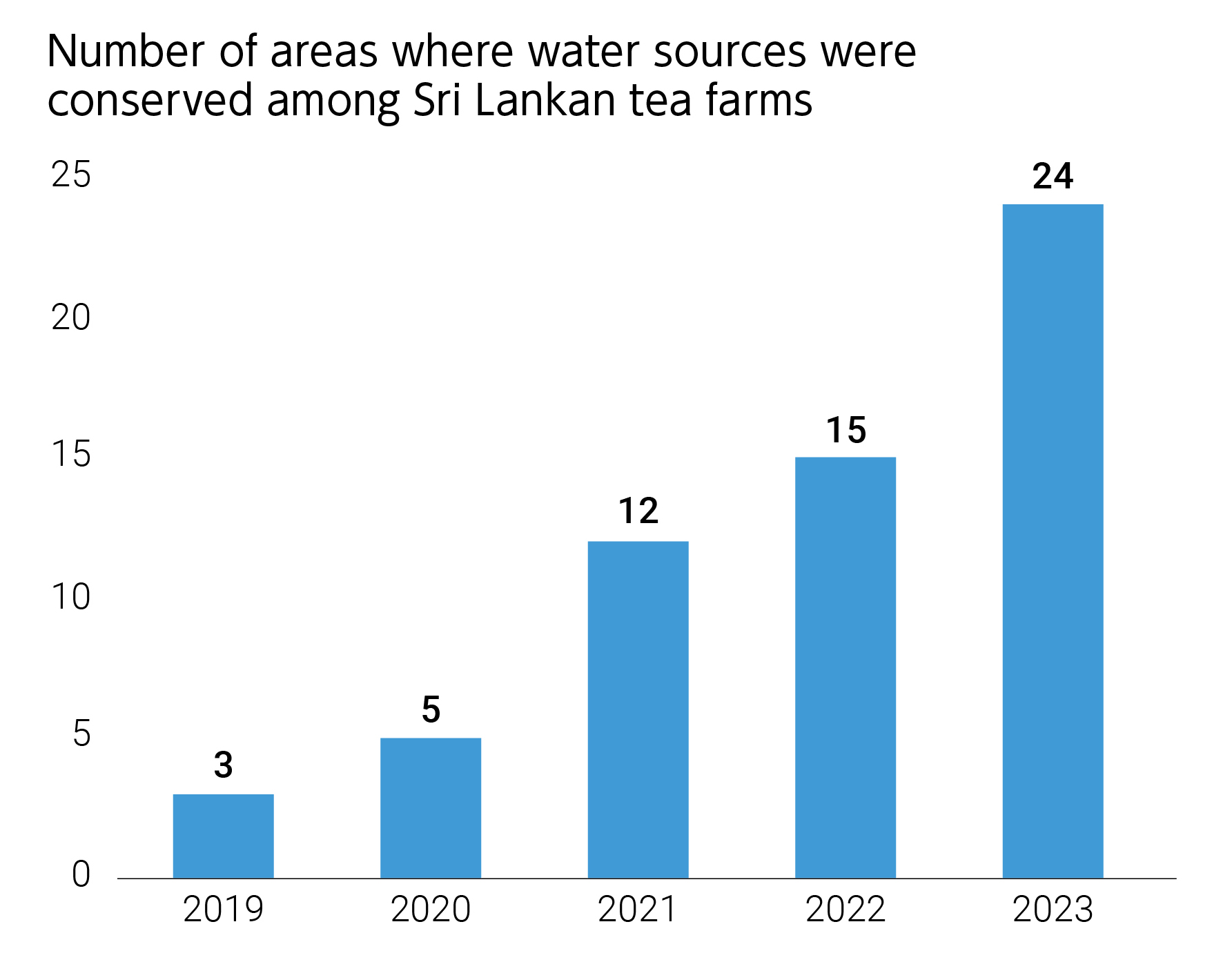
- We had completed the conservation of water sources at 15 locations in tea farms in Sri Lanka as of the end of 2022, and distributed pamphlets to raise awareness for local residents in water source areas (approximately 15,000 people) concerning the importance of water, its conservation, and the protection of basin regions.
- We are participating in the Corporate Engagement Program held by the Science Based Targets Network to develop scientific approaches and rules for setting targets related to water resources(Since 2021).
- At New Belgium Brewery in Colorado (US), where water stress is extremely high, we conducted a scenario analysis workshop at the request of the TNFD (2023: the details of this workshop were published in beta v0.4 of the TNFD Framework).
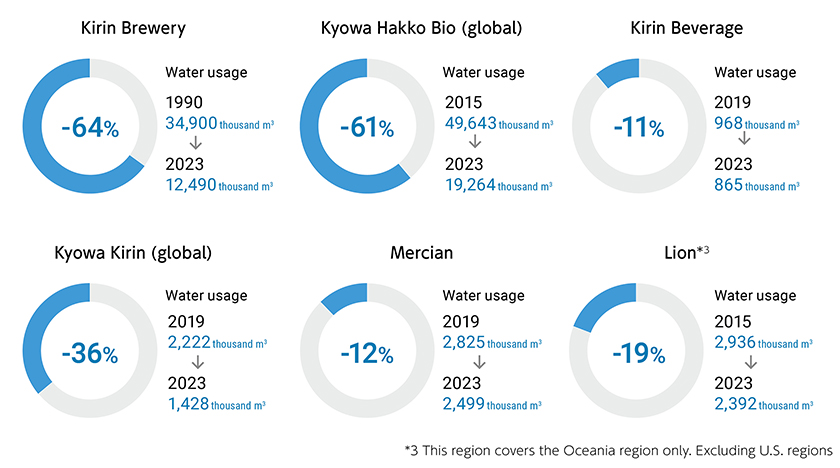
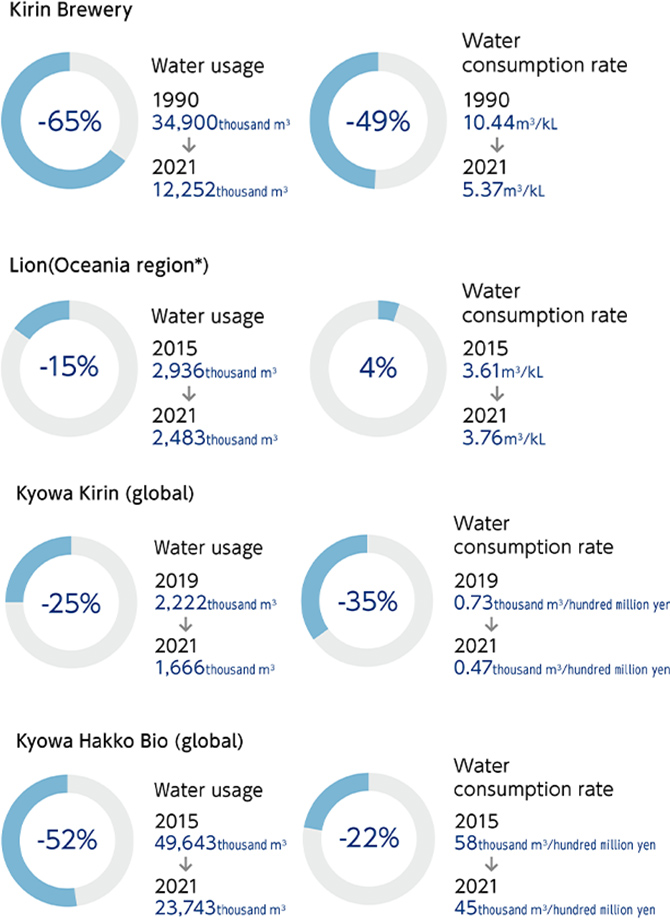
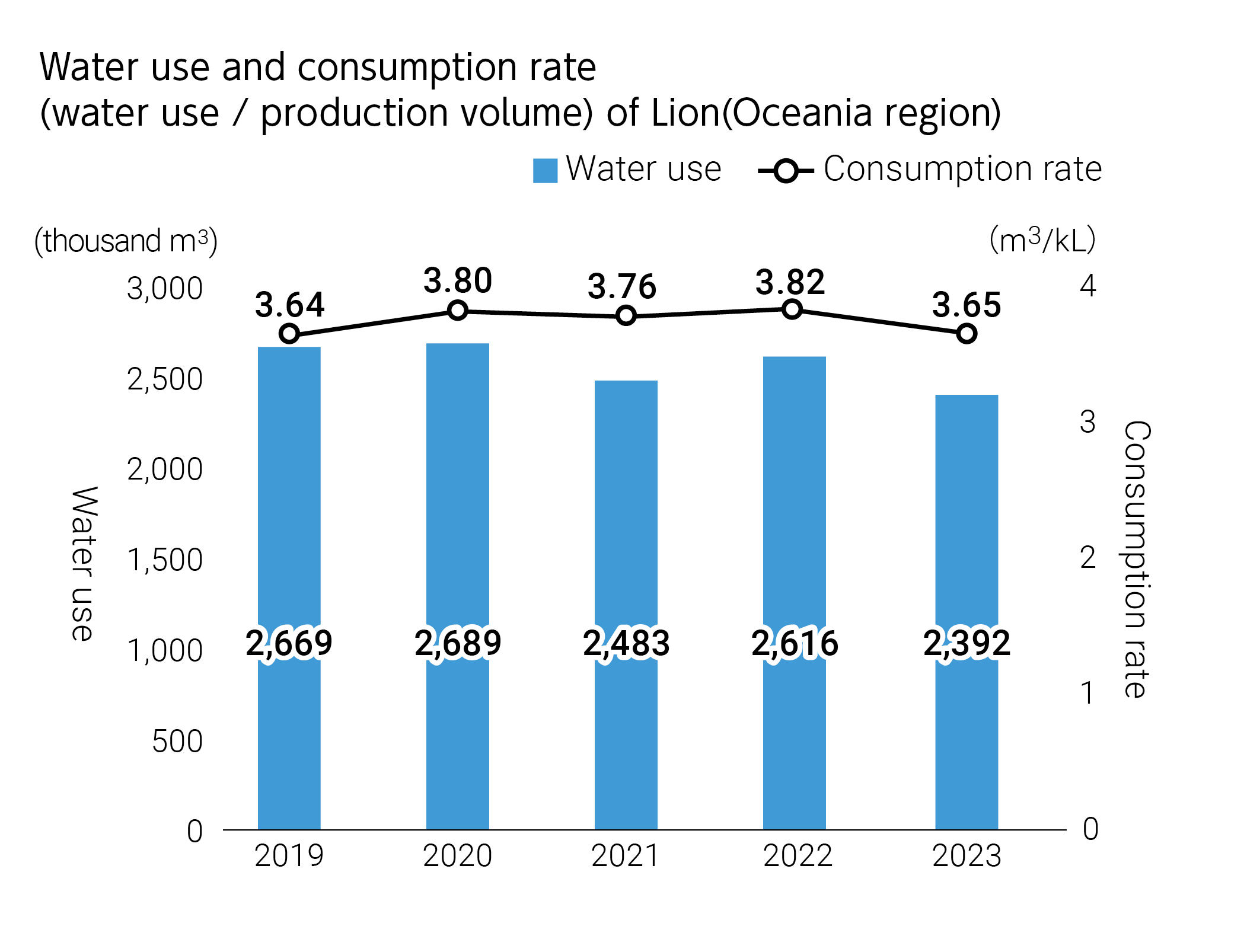
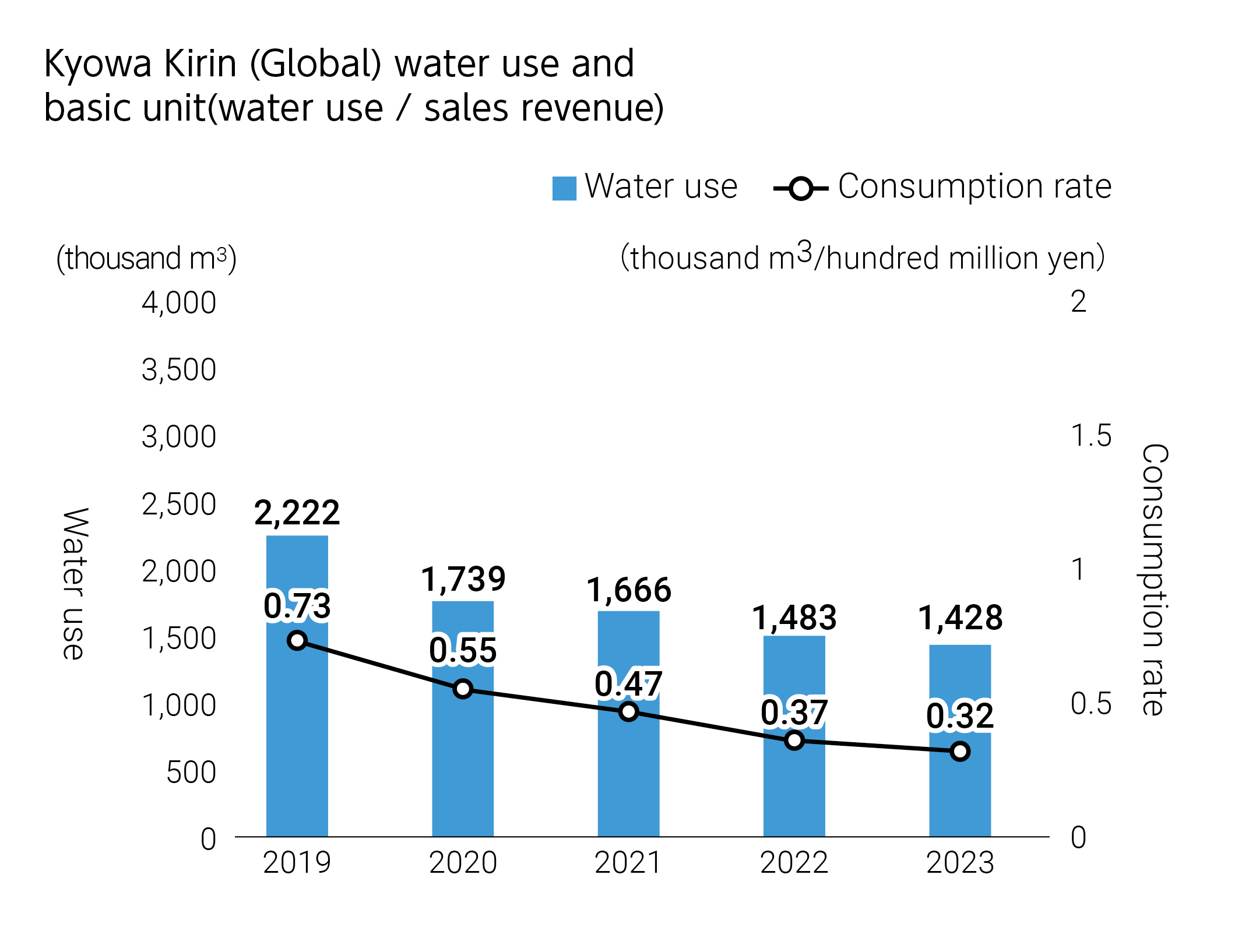
- Although the water consumption rate at Lion, one of our non-financial targets for water, increased compared with 2021, we are continuing efforts to achieve our targets.
- Continued efforts to conserve biodiversity through "Water Source Conservation Forest Activities", groundwater recharge, etc.
Targets and Progress
Water consumption rate at production sites and breweries with high
levels of water stress (Lion)
2025: Less than 2.4kl/kl (CSV commitment)*1
2025: 2.4kl/kl or less (non-financial target)*2
2024: 3.0kl/kl or less (non-financial target)*2
- Tooheys Brewery,Castlemaine Perkins Brewery, James Boag Brewery, Pride
- Tooheys Brewery,Castlemaine Perkins Brewery, James Boag Brewery
Actual results
Materiality analysis of water sources
Conservation activities for water sources on tea farms
As a first step in solving water issues in areas where we source our agricultural raw materials in the upstream of our value chain, the Kirin Group began water source conservation activities at Sri Lankan tea farms in 2018.
We had completed conservation activities at 15 sites at the end of 2022. We have provided group training to 1,750 people living near water sources in order to support understanding of the necessity of conserving water sources. In addition, we have distributed pamphlets on water conservation and basin protection to 15,000 residents as part of measures to raise awareness.
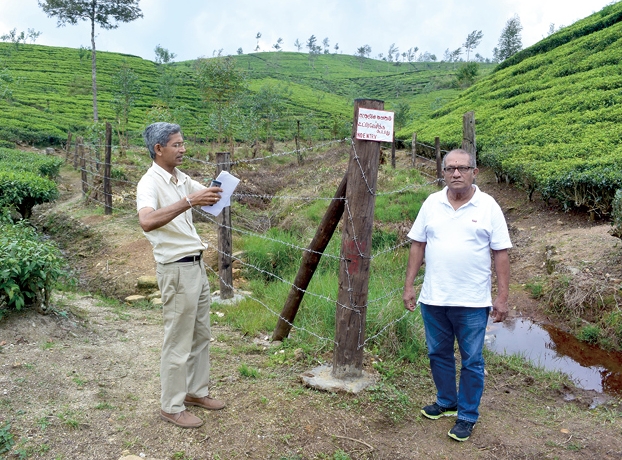
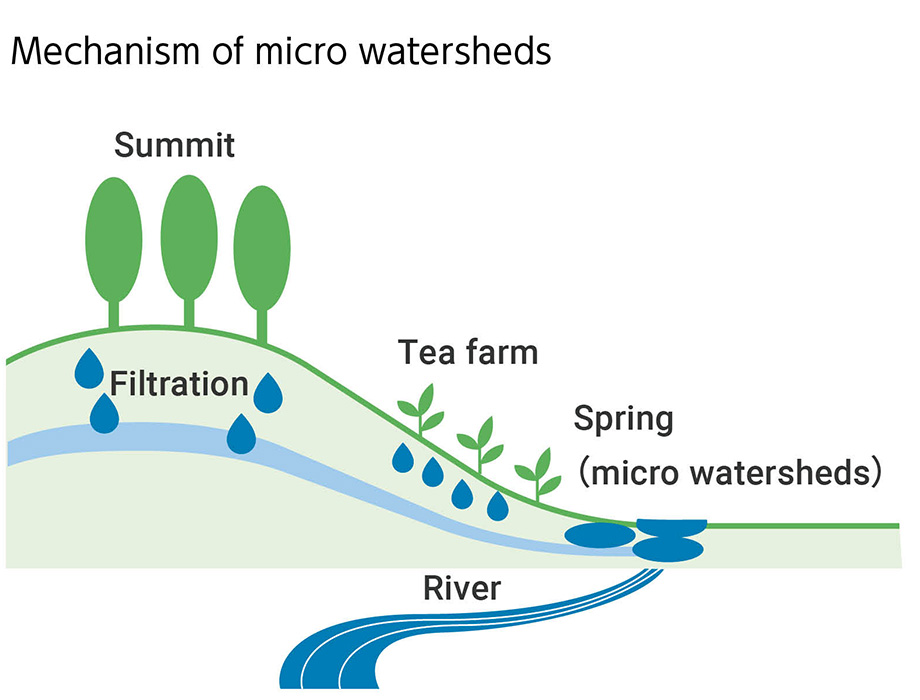
At the tea farms in the Sri Lankan highlands, there are many areas with tea trees on steep slopes. In places with good conditions such as strata, however, rainwater penetrates into the ground and gushes out as springs in certain places in tea farms. These places are known as micro watersheds. Micro watersheds on tea farms can be found in the highlands of central Sri Lanka, and, in almost all cases, they are headstreams of rivers flowing through coastal cities. For this reason, while they occupy only a tiny area, they are very precious water sources.
As part of our support for the acquisition of Rainforest Alliance certification by Sri Lankan tea farms, we are engaging with farm managers every year.
We learned that although the Sri Lankan government went as far as mapping micro watersheds in order to support understanding of their importance and make them easier to conserve and manage, these efforts were held up owing to a lack of funds.
Therefore, in order to further enhance the sustainability of tea farms whose acquisition of certification we supported and the surrounding areas, we began activities to conserve water sources at farms in 2018.
These activities involve fencing off micro watersheds of the farms so that they are not used for other purposes, and planting unique regional native species around them. This provides a diversity of vegetation at tea farms, which have a single crop, and prevents soil from flowing down the mountain slope into water sources as a result of torrential rain, etc.
Education programs to teach the value of water
The Kirin Group is conducting an education program to teach residents living near target water sources about such matters as the importance of water and the functions of micro watersheds. At some farms, we are also working to incorporate our educational programs as part of the curriculums of day care centers and elementary schools attended by the children of tea pickers, etc. We have achieved our initial target of 15,000 people and plan to expand the program further.
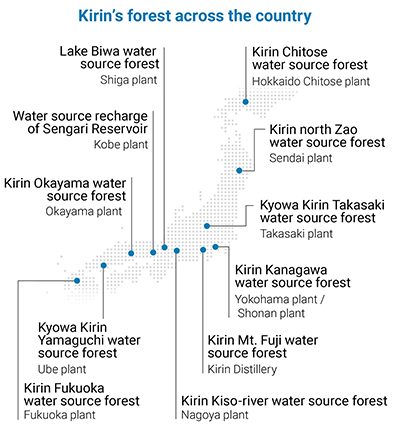
Water Source Forest Conservation Activities
Our "Water Source Forestation Conservation Activities", which are an activity to protect the water sources of our breweries and plants, began in the forest of the Tanzawa district of Kanagawa Prefecture, which is the water source for Kirin Brewery’s Yokohama Plant in 1999. We have adopted this initiative, which was a pioneering initiative in the industry, in 11 locations across Japan. Under medium and long-term agreements with the local governments and other relevant parties that manage the water source forests, the program includes tree planting, undergrowth cutting, pruning, and thinning. Today, many of the forests are bright, luxuriant forests. In some locations, some of our customers have volunteered to take part in the activities.
-
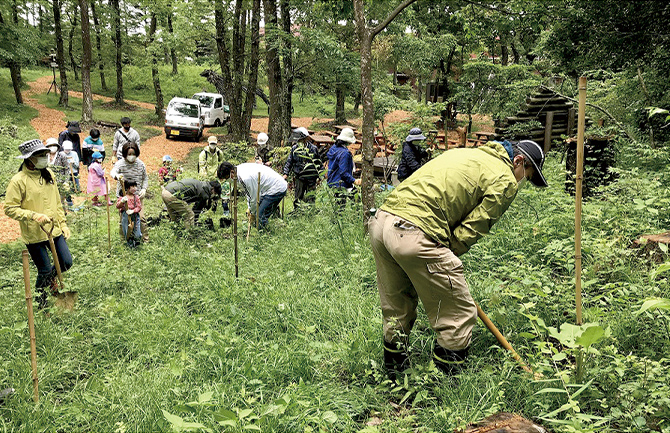

Water Source Conservation Forest Activities at Kirin Mt. Fuji water source forest
-
Grassland conservation activities to recharge groundwater
In the "Aso Area Grassland Regeneration Project Aimed at 'World Cultural Heritage' states," we are providing "support for the resumption of open burning" to preserve the grassland landscape of Aso.
Preserving the vast grasslands of Aso, which recharge large amounts of groundwater, will help protect the water that we use as a raw material at the Mercian Yatsushiro Plant.
In 2022, five people from the Yatsushiro Plant participated in this activity. Maintaining grasslands not only nurtures groundwater, but also protects habitats for a wide variety of flora and fauna, including endangered species.
-
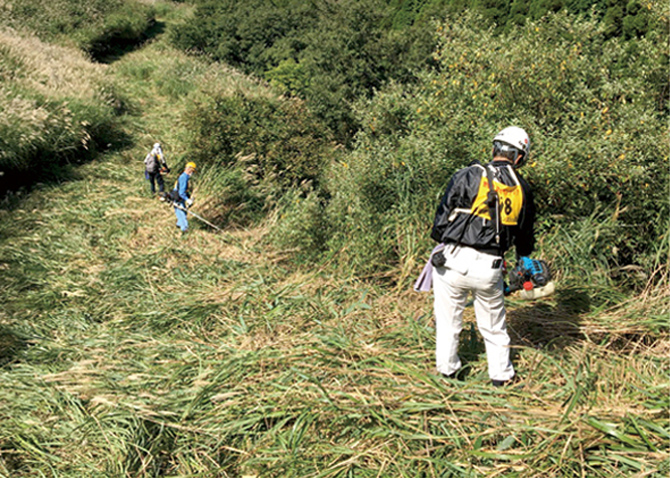

Cutting paths around areas for controlled burning
-
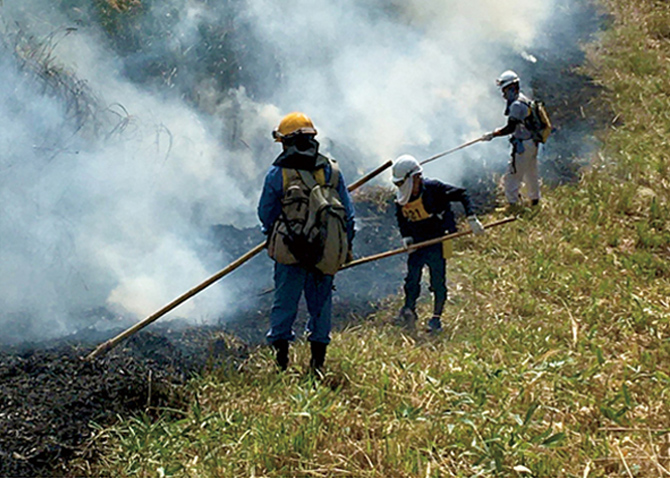

Controlled burning
Production
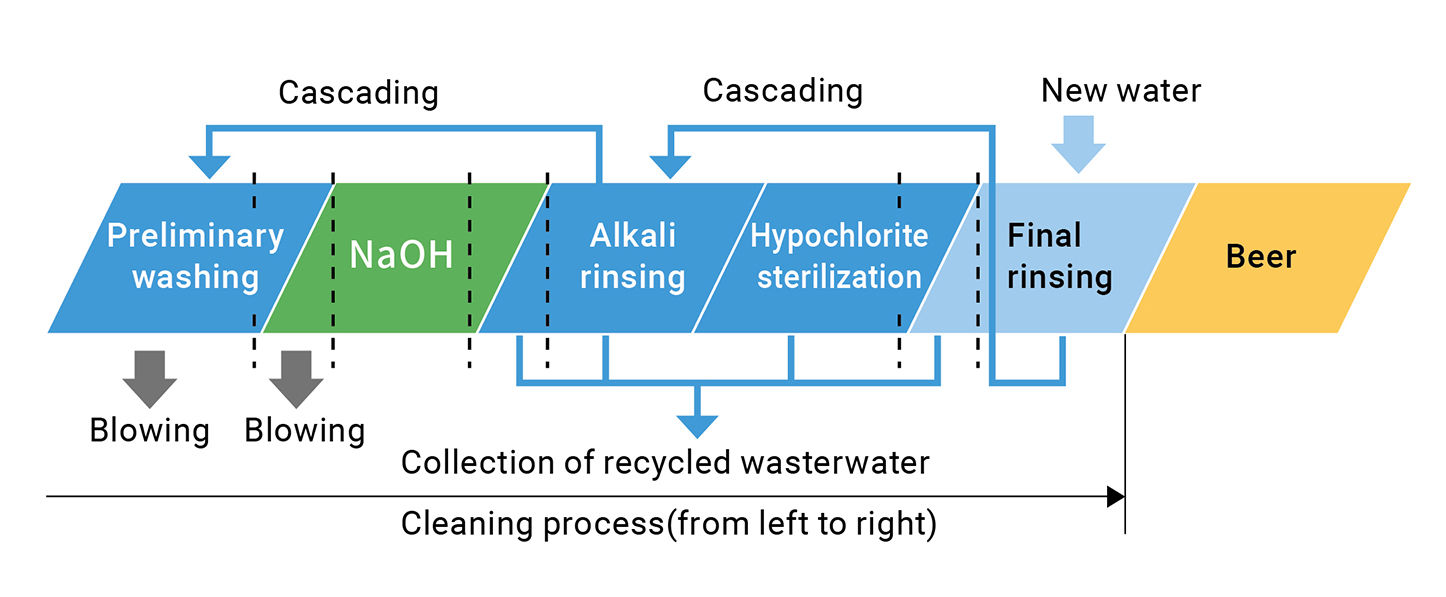
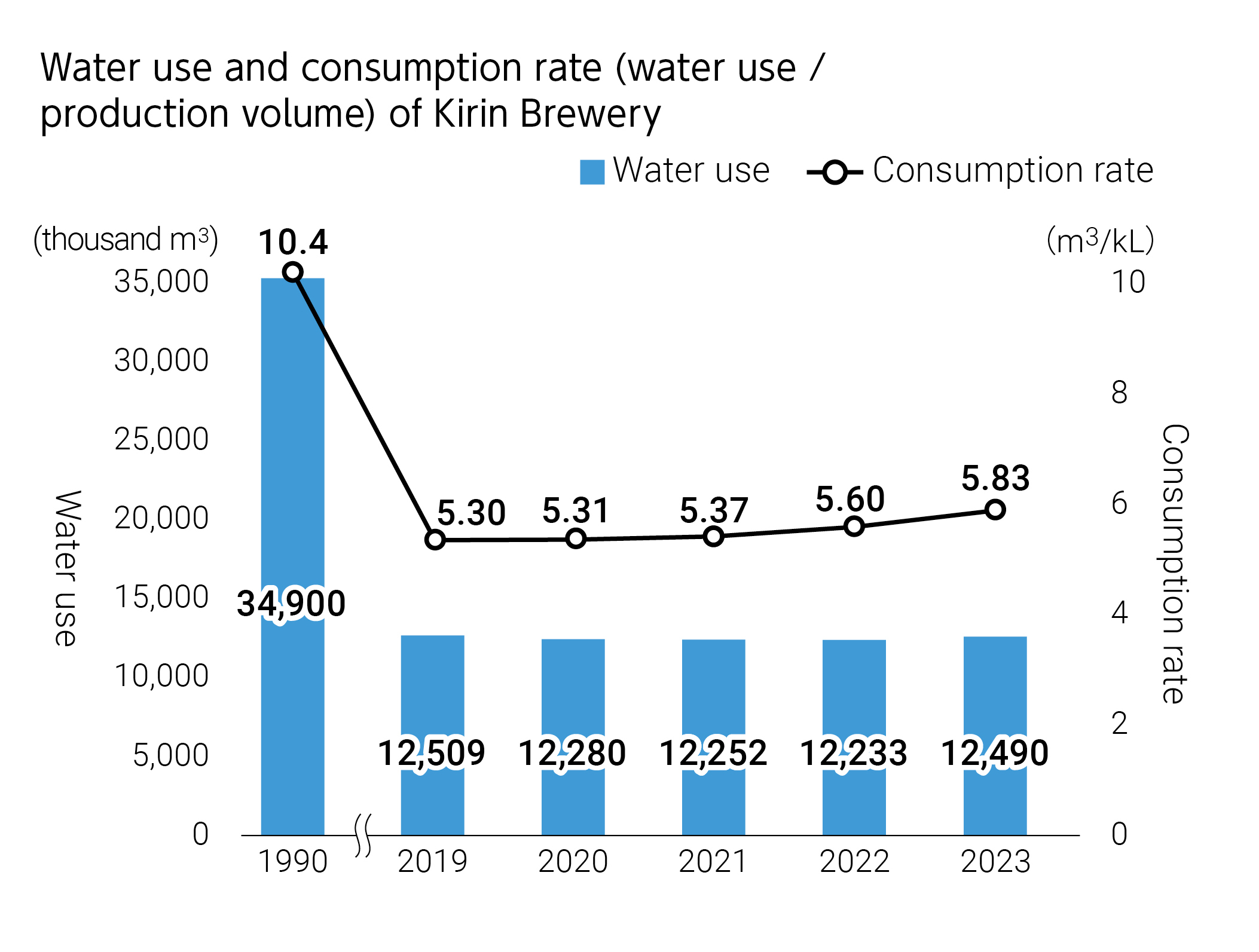
In plants, much of our water usage is for washing and sterilizing processes for equipment and pipes. In addition to establishing frameworks and mechanisms to confirm and assure the washing from a quality perspective, we strictly control water flow rate and velocity to ensure that we do not waste water. We also actively pursue the re-use of water, depending on the purpose. For example, the rinsing water that we use in the final step of the pipe and equipment washing process is still relatively clear, so we can use it again for the initial process of pipe washing. In this way, we have implemented a cascading system of water use in which we repeatedly use water that we have previously used in washing, according to the quality of the water. In actuality, considerable knowledge on how to use equipment is necessary to guarantee that we are properly washing the equipment and pipes, such as achieving the right balance of the amount of water we can recover and the amount of water we can use, as well as the timing of recovery and use.
The Kirin Group is achieving a high level of water conservation by sharing and accumulating various different types of expertise.
In 2009, Lion partnered with the government of Queensland, Australia, to install a reverse osmosis (RO) plant at the Castlemaine Perkins Brewery, to recover wastewater and minimize our reliance on mains-fed town water in order to minimize water use in brewery areas with very high water stress. Lion has introduced a water recycling plant with the aim of reducing the amount of water used for brewing by half. We use water treated with reverse osmosis membranes in non-product related processes, such as cleaning, cooling, and pasteurizing.
Wastewater and the usage of biogas
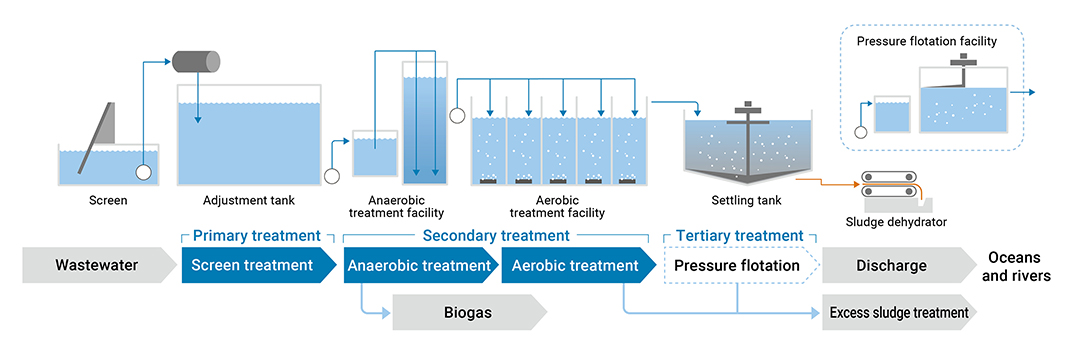
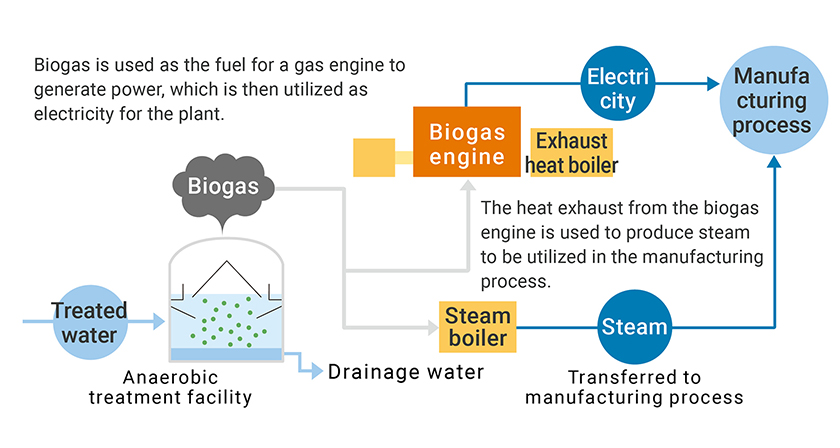
In the Kirin Group, we purify the water that we have finished using to voluntary standards that are stricter than those required by law, before we release it into rivers and sewers. Breweries and plants in basin areas with strict wastewater standards remove phosphorus and solids by anaerobic and aerobic treatment followed by pressure flotation. We reuse excess sludge discharged from aerobic and pressure flotation treatment as fertilizer and soil conditioner. The Kirin Group discharges clean water into the ocean, rivers, and sewers in consideration of the aquatic ecosystem. In our breweries, we have introduced anaerobic treatment facilities to purify the wastewater generated by the production process.
Unlike conventional aerobic treatment, anaerobic treatment does not require electricity for aeration. Also, the anaerobic microorganisms generate biogas as a by-product of the treatment process. This biogas, the main component of which is methane, can be utilized in biogas boilers and cogeneration systems. Biogas is derived from plant materials such as malt and is classified as a renewable energy source because the CO2 emitted from biogas combustion originally absorbed by plants from the atmosphere is simply returned to the atmosphere.
Enviromental protection activities in basin regions
At the various production plants of the Kirin Group, we are conducting a range of environmental protection activities, particularly riverside clean-up activities in cooperation with local governments and NGOs.
At our breweries and plants, including those of Kirin Brewery, Kirin Beverage, Mercian, Kyowa Kirin, and KOIWAI DAIRY PRODUCTS, we are engaged in local environmental beautification and environmental protection activities, focusing on the rivers they draw water from and other nearby rivers.At the Kyowa Hakko Bio Yamaguchi Production Center, employees performed clean-up activities in the waters off Hyakken, a port facility where chemicals and glucose solutions are unloaded.
-
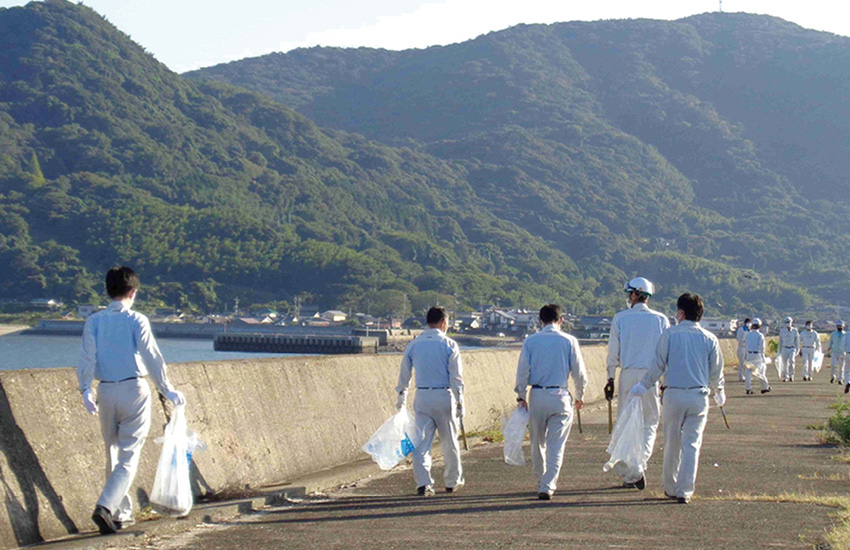

Clean-up activities off Hyakken